Table of Contents
How does PRP injection work, and what is it?
Introduction to understanding PRP injection
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) is a blood preparation that has garnered traction as a therapeutic agent in recent years. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a platelet concentrate derived from the patient’s blood. It contains numerous growth factors and bioactive proteins crucial in tissue repair and regeneration. A simple blood draw is followed by centrifugation to separate the distinct types of blood cells. Then, the resultant platelet concentrate is injected into the afflicted area to promote recovery.
Production of PRP
PRP preparation entails a series of stages crucial to the final product’s efficacy. Blood is typically drawn from the arm of the patient in the initial phase. The blood sample is then inserted in a centrifuge that spins rapidly to separate the various types of blood cells. After the initial rotation, the platelet-containing plasma is separated from the red and white blood cells. The plasma is then spun a second time to concentrate the platelets further. Finally, the resultant PRP concentrate is injected into the afflicted area to promote healing.
Action mechanism
PRP unleashes growth factors and bioactive proteins essential for tissue repair and regeneration. The increased concentration of growth factors stimulates cell growth and the formation of new blood vessels, both vital for wound healing. The PRP also contains cell adhesion molecules, aiding stem cell recruitment to the injured area. Once stem cells arrive, they differentiate into the proper cell type and promote tissue repair.
Medical Applications
PRP has numerous medical applications, including orthopedics, dermatology, dentistry, sports medicine, neurology, ophthalmology, and plastic surgery.
Constraints and Dangers
While PRP has shown promise in treating various conditions, there is insufficient evidence to support its efficacy in most instances. In addition, PRP therapy outcomes highly depend on the age, health, and severity of the patient’s injury. Furthermore, PRP therapy may not be appropriate for all patients, and there are dangers associated with the procedure, such as infection, pain, and bleeding.
PRP Injection: Therapeutic Applications
Orthopedics
PRP has been utilized to treat numerous orthopedic conditions, including knee osteoarthritis, ruptured tendons, and ligament injuries. PRP’s elevated concentration of growth factors can stimulate tissue repair and regeneration, which is essential to healing. Platelet-rich plasma injections are administered directly to the injured area to expedite recovery.
Dermatology
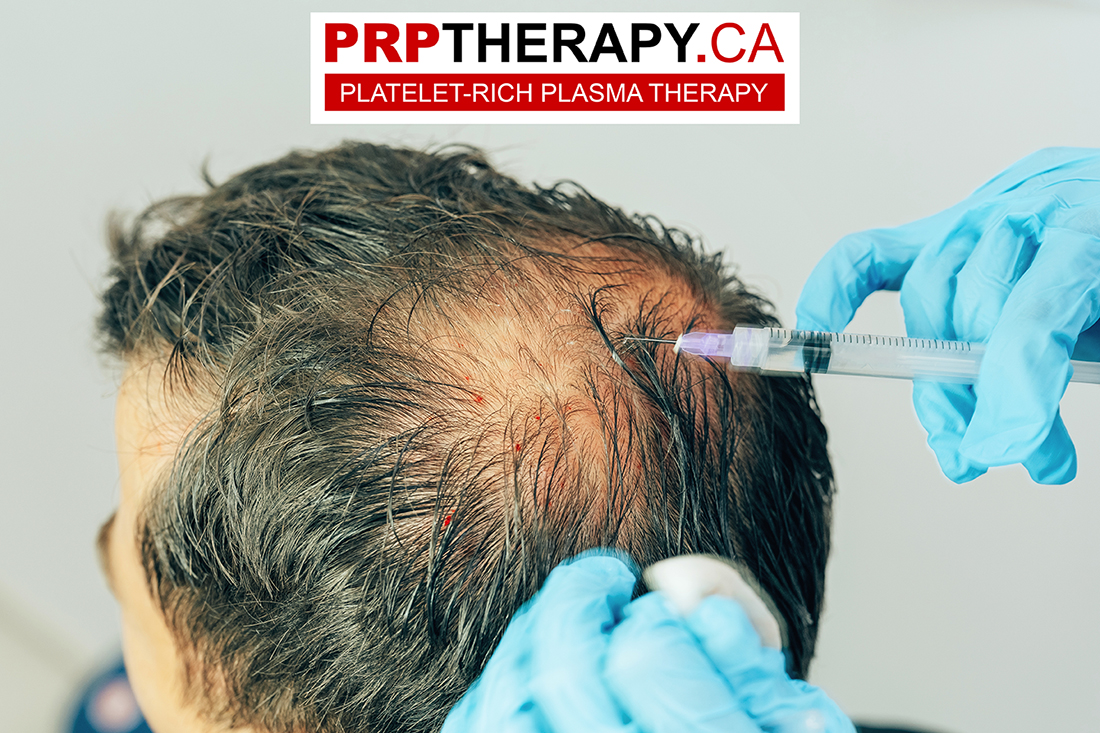
As a cosmetic treatment for wrinkles and hair loss, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) has acquired popularity. PRP injections are administered to the scalp in hair loss cases to stimulate hair growth. The increased concentration of growth factors encourages hair growth and enhances the condition of existing hair.
Dentistry
In dentistry, PRP has been utilized to promote tissue regeneration and repair. For example, dental implant procedures, bone grafting, and periodontal surgery encourage healing and reduce infection risk.
Athletics Medicine
PRP has been used to treat numerous sports-related injuries, such as muscle strains and ligament fractures. PRP’s increased concentration of growth factors can expedite the healing process and decrease the danger of further injury.
Neurology
PRP has been studied as a potential treatment for neurological disorders, such as proliferative diabetic retinopathy. The elevated concentration of growth factors in PRP can facilitate the growth and repair of soft tissues, such as tendons, ligaments, and muscles. PRP is a popular treatment for sports injuries like muscle strains, ligament sprains, and tendon fractures. It has also been utilized in treating chronic conditions, including tennis elbow, golfer’s elbow, and knee osteoarthritis. Injections of platelet-rich plasma (PRP) have acquired popularity in sports medicine due to their ability to accelerate recovery and allow athletes to resume regular activity sooner. Many renowned athletes, such as Tiger Woods and Kobe Bryant, have used PRP therapy to aid in their recovery from injuries.
In addition to its applications in sports medicine, PRP has been utilized in other medical disciplines. For example, injections of PRP have been used to treat hair loss and creases in dermatology. PRP can stimulate hair growth in individuals with androgenic alopecia by increasing blood flow to hair follicles and promoting the multiplication of hair follicle cells. In addition, PRP can stimulate collagen production for wrinkles and enhance skin texture and elasticity.
In dentistry, PRP has been used to promote tissue regeneration and growth. For example, it can accelerate the healing process following oral surgery and regenerate bone and soft tissue in the mouth.
Neurology is another discipline that has demonstrated an interest in PRP usage. For example, PRP may be advantageous in the treatment of certain neurological conditions, such as proliferative diabetic retinopathy, by stimulating the development of new blood vessels in addition to enhancing the blood flow to the affected area; this treatment reduces inflammation.
The use of PRP has also been investigated within the field of ophthalmology. It has been utilized to treat various eye conditions, including dry eye syndrome, and promote corneal lesions’ healing. PRP has also been utilized in plastic surgery to facilitate tissue regeneration and repair. In addition, it has been used to treat incisions, burns, and scars and to enhance the results of other cosmetic procedures such as facelifts and breast augmentation.
Advantages and Disadvantages
As with any medical treatment, PRP has both benefits and drawbacks.
Positives of PRP
One of the most significant benefits of PRP is that it utilizes the patient’s blood cells, eliminating the danger of rejection or allergic reaction. Furthermore, the PRP procedure is minimally invasive and can be performed in an outpatient setting so that patients can rapidly return to their normal activities. In addition, PRP is a natural substance containing bioactive proteins and growth factors that can promote tissue repair and regeneration.
Disadvantages of PRP
Insufficient scientific evidence exists to support the efficacy of PRP in some instances, which is one of its primary drawbacks. While numerous studies have yielded encouraging results, additional research is required to fully comprehend PRP’s efficacy in treating various conditions. In addition, the entire procedure, from the blood draw to the injection, can be time-consuming. Multiple sessions may be required to attain the intended results in certain instances.
Potential Risks
A few potential hazards are associated with PRP therapy, despite the treatment’s general safety. Pain, edema, and bruising at the injection site are typical adverse effects. In uncommon instances, infection or nerve injury may occur. Before undergoing PRP treatment, patients should discuss the potential risks and benefits with their doctor.
Price, Supply, and Regulation
Cost of the PRP procedure
The price of PRP therapy can vary based on the treatment type, area, and several sessions required. The cost of PRP injections per session can range from several hundred to thousands of dollars. Depending on the specific insurance plan and the ailment being addressed, insurance coverage for PRP treatments can vary. Certain medical conditions, such as knee osteoarthritis and proliferative diabetic retinopathy, may be covered by the cost of PRP treatments under specific insurance policies. Nevertheless, insurance plans typically do not cover PRP as a cosmetic procedure. Patients should contact their insurance provider to ascertain if PRP therapy is covered under their policy.
The cost of PRP treatments can vary depending on the treatment area and the number of sessions required. Due to the additional preparation and apparatus necessary, PRP treatments are typically more expensive than conventional treatments. However, the cost of PRP treatments may be justified for patients seeking a more natural and effective alternative to traditional therapies.

Supply
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) treatment availability also differs based on location and provider. PRP treatments are more broadly accessible in major metropolitan areas, and board-certified dermatologists, plastic surgeons, and other medical professionals may offer them. Patients must always ensure they are receiving PRP therapy from a qualified and experienced medical professional.
Regulation
Regulatory concerns and requirements for PRP treatment differ from country to country. PRP is not currently regulated by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the United States, although the FDA has approved certain PRP injection devices for specific uses. Therefore, patients should always verify that their medical provider utilizes FDA-approved equipment and follows proper safety protocols.
PRP is a promising treatment option for many medical and cosmetic conditions. Even though there is still much to learn about the efficacy of PRP, current scientific evidence suggests that it can play a significant role in facilitating healing and tissue repair. As research continues and new developments emerge, PRP will likely become an even more popular and versatile treatment option for in-need patients.
Conclusion
Platelet-rich plasma therapy is a type of regenerative medicine that has gained popularity in recent years for its potential to promote healing and tissue repair. PRP is prepared by taking a small blood sample from the patient’s arm and using a second spin to concentrate the platelets and various growth factors found in the patient’s own blood. The resulting rich plasma is then injected into the affected area, where it may play an important role in reducing symptoms and promoting healing. While PRP has been used successfully in famous athletes for torn tendons and other types of tissue damage, there is not enough evidence to support its effectiveness in treating stress-related hair loss. However, many people, including women, have reported positive results from the use of PRP for alopecia. Additionally, PRP has been used in conjunction with hyaluronic acid and local anesthetic to treat osteoarthritis. Health care providers and board-certified dermatologists should be consulted before undergoing any type of PRP treatment.